Coastal and Oceanic Landforms
- Abyssal fan – An underwater deposit of sediment formed by water currents
- Abyssal plain – A flat, smooth underwater surface that covers over 50% of the Earth’s surface. It forms the bottom of the continental rise and the top of the oceanic trench
- Archipelago – A group of islands
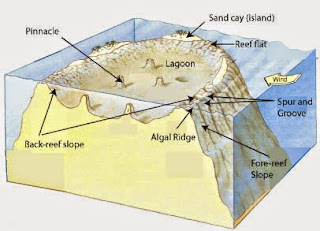
- Atoll – A ring-shaped coral reef
- Arch – A rock formation with an opening
- Ayre – A narrow beach across the ends of a shallow bay
- Barrier bar and barrier island – A flat formation of sand that is parallel to the coast
- Bay and gulf – A body of water connected to an ocean but surrounded on most sides by land
- Beach and raised beach – The land along the edge of a body of water, consisting of loose rocks or sand.
- Beach cusps – Sediment in an arc shape on the shore, caused by the wave action
- Beach ridge – A ridge running parallel to the water’s edge, caused by wave action
- Bight – A recessed area in a coastline
- Blowhole – A hole in the end of a sea cave
- Channel – A narrow body of water
- Cape – A portion of land that extends into the sea or ocean
- Calanque – A steep cove
- Cliff – A vertical wall of rock
- Coast – Where the water meets the land
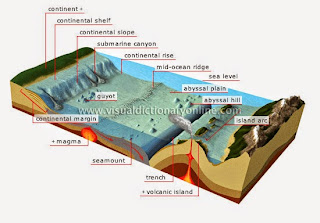
- Continental shelf – The extended edge of each continent which is underwater
- Coral reef – Underwater formations of calcium carbonate
- Cove – A small bay
- Cuspate foreland – An accumulation of sand and gravel forming a land body that extends like a “finger” into the body of water
- Dune system – Groups of sand dunes
- Estuary – A semi-enclosed body of water with a connection to the sea and with at least one inbound source of water
- Firth – A large bay
- Fjard – A short, shallow and broad fjord
- Fjord – a long narrow inlet with steep cliffs
- Headland – A point of land that extends into a body of water and has a steep drop
- Inlet – A connection between a bay and the ocean
- Island, islet – A portion of land that is surrounded on all sides by water
- Islet – A rock that is surrounded on all sides by water
- Isthmus – A narrow strip of land with water on each side
- Lagoon – A shallow body of water
- Machair – The grassy fields that are inland from a dune ridge
- Marine terrace – A flat, often slightly inclined, surface with a slight slope on the water side and a steeper slope on the land side
- Mid-ocean ridge – An underwater mountain system
- Ocean – A body of salt water
- Oceanic basin – A basin that is below sea level
- Oceanic plateau – A flat rock formation that is above the continental slope
- Oceanic trench – A long, narrow opening on the ocean floor
- Peninsula – A piece of land that has water on three sides
- Ria – A river valley that is open to the sea
- River delta – A deposit of sediment at the mouth of a river where it flows into a larger body of water
- Salt marsh – An area between the saltwater sea and a piece of land that is flooded by salt water
- Sea – The salty water that covers 70% of the Earth
- Sea cave – A cave at the edge of the sea that is formed by wave action
- Seamount – An underwater mountain
- Shoal – A sandbar
- Shore – Where the water meets the land
- Sound – A large ocean channel between two bodies of land
- Spit – A piece of land that extends into water
- Strait – A narrow waterway that connects two larger bodies of water
- Strandflat – The low land on the actic and antarctic coasts
- Submarine canyon – A steep valley in the sea floor
- Surge channel – A very narrow opening in the rocks of the shoreline
- Volcanic arc – A chain of volcanoes positioned in a slightly curved layout
- Wave cut platform – The flat area at the base of a cliff created by the waves